Filter press Plate and frame | Filter press plate material
Filter press plate material
VisitCount 64
Historically, filter presses were constructed using a series of frames and simple rectangular plates, These plates featured channels or grooves on their surface to guide and discharge liquids. This design led to the term plate-and-frame filter presses, a term still used today in some contexts. In this structure, solids would accumulate on filter cloths placed between the frames and plates. Once the frames were filled, the plates were separated, and the solid cake was discharged.
Although effective initially, the plate-and-frame design had limitations in solid-liquid separation and dewatering. While this type of press is still used in some industries, modern manufacturers increasingly prefer recessed plates (chamber plates) or membrane plates, which offer higher efficiency and easier maintenance.
What is a Filter Press Plate?

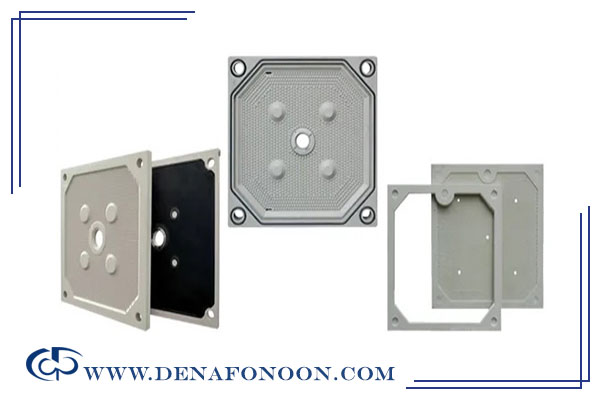
Plates are a core component of a filter press, and their quality, material, and design directly affect overall filtration performance. Feed holes, distribution channels, and drainage pathways vary depending on the material and design. Standard plate sizes include:
- 200 × 200 mm
- 400 × 400 mm
- 600 × 600 mm
- 800 × 800 mm
- 1000 × 1000 mm
- 1200 × 1200 mm
- 1500 × 1500 mm
Custom sizes can also be manufactured to meet specific industrial requirements. All plates are square in shape.
Types of Filter Press Plates

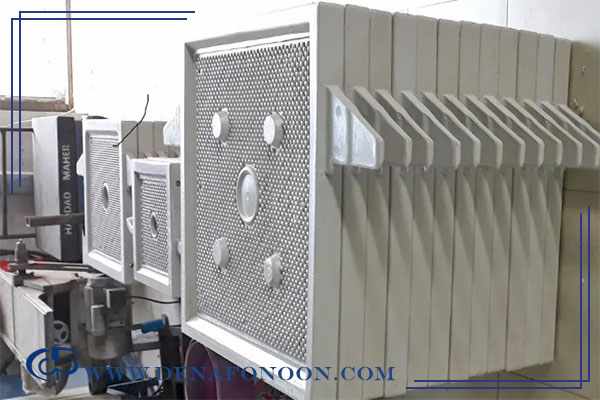
Filter press plates generally fall into two main categories:
1.Plate-and-frame type
2.Recessed (chamber) plates
Plate-and-Frame Filter Press Plates
One of the earliest and most widely used types of filter presses was the plate-and-frame model, This design consists of alternating flat plates and frames. The frames create a cavity for the filter cake, while the plates hold the filter cloth. Slurry is pumped into the frames, solids are retained, and liquid passes through the cloth to exit the plate channels.
Key features include:
- Simple, easy-to-understand design
- Compatibility with various types of slurry
However, manual opening and closing of these plates made operation time-consuming, Cleaning and replacing filter cloths was also labor-intensive, With technological advancement, these plates have gradually been replaced by recessed plates (chamber) and membrane plates, offering better efficiency and easier maintenance.
Recessed (Chamber) Filter Press Plates
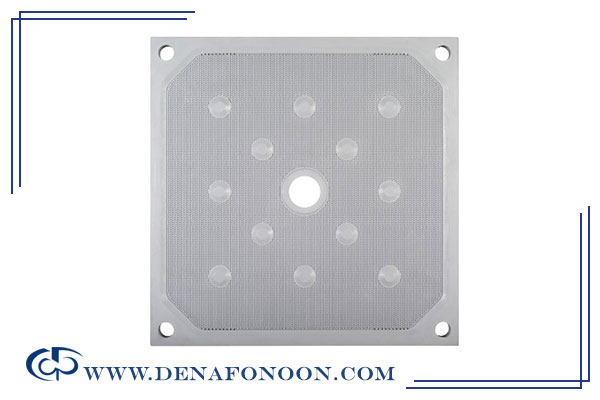

Recessed plates, also called chamber plates, differ from plate-and-frame plates by having a built-in recessed area to form the filter cake cavity, eliminating the need for separate frames. When plates are pressed together, a chamber is created for solids to accumulate.
The recessed design allows slurry to be pumped into these chambers. Solids remain in the recess, while liquid passes through the filter cloth and exits via plate channels. Typically, the recess depth is around 15 mm to reduce stress on the filter cloth, and the final cake thickness can reach up to 32 mm, depending on the process, Filter presses that are built using chamber plates are referred to as chamber filter presses.
Membrane Filter Press Plates
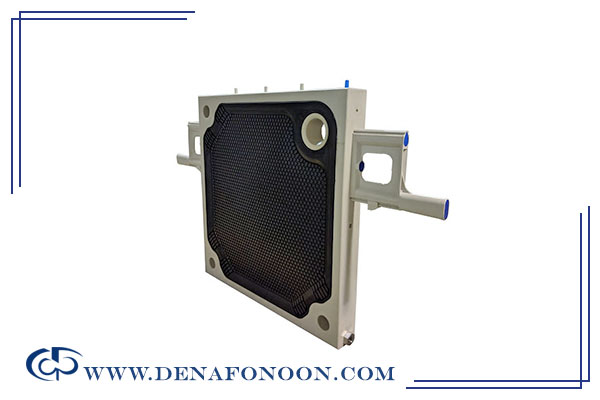

Membrane plates are an evolution of recessed plates, designed to improve solid-liquid separation and dewatering efficiency, Like chamber plates, they have recessed areas, but their surfaces are flexible, allowing expansion into the cavity between plates.
The filtration process begins similarly to chamber plates: slurry is pumped into the plates, and solids accumulate. Then, air or water pressure expands the flexible membrane, compressing the solids further and extracting more liquid.
Benefits of membrane plates include:
- Drier filter cakes with lower moisture content
- Shorter filtration cycles
- Improved cake washing quality
- Increased production capacity and speed
Membrane plates are available in various sizes and designs to suit different operational requirements. Feeding options include central, corner, or side inlets, and multiple discharge methods are available, increasing flexibility for industrial applications, Filter presses that use membrane plates are commonly referred to as membrane filter presses.
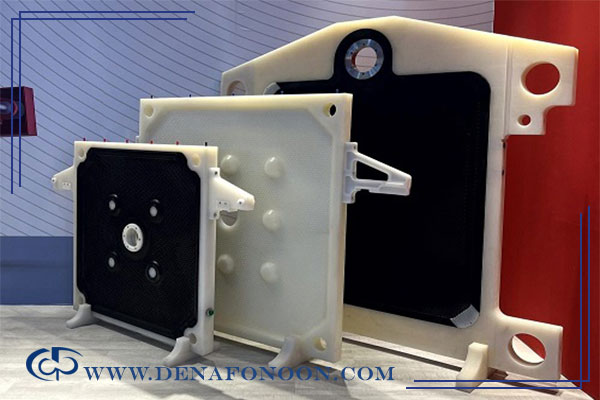
Polypropylene Filter Press Plates
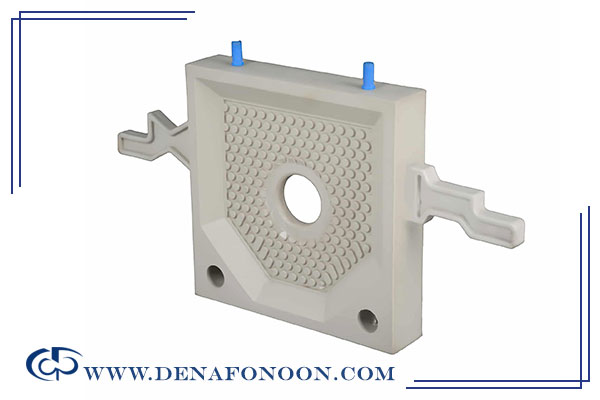

Polypropylene (PP) plates are lightweight, durable, and highly chemical-resistant, making them ideal for industrial filtration. Their advantages include:
- Lightweight: Reduces filtration cycle time
- Easy cleaning: Low water absorption allows fast maintenance
- Reliable sealing: Precision machining ensures leak-free operation
- High capacity: Chemical and thermal resistance enhances performance
- One-piece construction: Minimizes risk of cracking or leakage
- Variable sizes: From 200 × 200 mm to 2000 × 2000 mm
- Adjustable cake thickness: 20–60 mm, depending on the material
- High temperature tolerance: Up to 90°C
- Wide pressure range: 4–30 bar
- Flexible feeding and discharge: Central or corner feed; open or closed discharge
- Membrane options: For applications requiring very low cake moisture
Cast Iron Filter Press Plates:
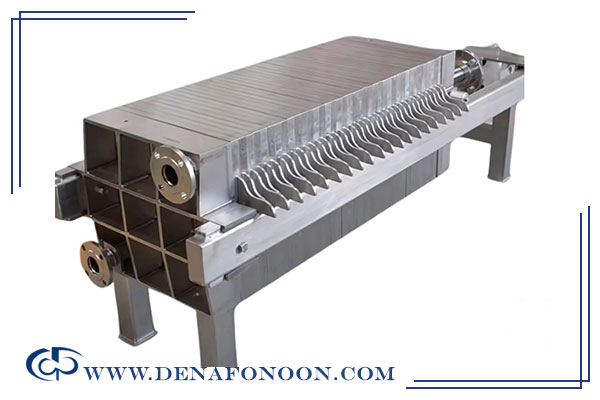

For filtration of high-temperature slurries above 120°C, polypropylene plates are not suitable. Cast iron plates, made of high-quality or nodular cast iron, are recommended.
Advantages:
- High thermal resistance
- Strong mechanical properties
- Long service life
- Available in manual or automatic discharge
Due to their heavy weight, automatic models are recommended for plates larger than 800 mm to reduce labor requirements.
Typical applications:
- Oil refining (white oil, glycerin)
- Metallurgy
- Ceramic industries (kaolin, activated bentonite, various clays)
Filter presses using cast iron plates are commonly referred to as cast iron filter presses.
Stainless Steel Plates:
The basic architecture, operating principles, and process technology of filter presses are consistent; the main differences lie in their structural and protective measures. Depending on the application—whether in chemical, pharmaceutical, or food industries—specific standards must be followed. Denafonoon stainless steel filter presses are designed and manufactured according to high hygiene and purity standards, ensuring compliance throughout all stages of processing and use.
In stainless steel models, in addition to the plates,all components in contact with the product are made from high-quality stainless steel, providing complete protection against corrosion. In certain cases, the entire unit can be constructed from stainless steel or fully coated with stainless steel to ensure enhanced durability and hygiene.
Advantages of Stainless Steel Plates
- High-quality construction and reliable performance
- Corrosion resistance for long-term use
- FDA-approved versions suitable for direct contact with food and pharmaceutical products
- Extended service life and high durability
- Easy cleaning and maintenance
- Compliance with specialized standards for chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries